- California, TX 70240
- info@gmail.com
- +123 456 7890

In today’s globally connected world, businesses often have teams, offices, and customers scattered across countries. While this distributed model enables flexibility and access to global talent, it also introduces one common frustration: network latency.
If you’ve ever experienced slow application loading times, lag in video calls, or delayed access to business-critical resources when connecting to offshore offices — you’ve faced the impact of latency.
Let’s break down why this happens and how Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) can fix it.
Why Does Network Latency Occur for Cross-Country Traffic?
Network latency refers to the time it takes for data to travel from one point to another. When your workforce in Dubai accesses a data center in India or your developers in Europe connect to servers in the US, several factors introduce delay:
- Physical Distance – Data packets must travel thousands of kilometers across undersea cables or satellite links, which naturally increases round-trip time.
- Multiple Hops & Routing – Cross-border traffic often goes through multiple ISPs, exchange points, and firewalls before reaching its destination, adding processing delay at each hop.
- Congestion & Bandwidth Bottlenecks – High network usage during peak hours can slow down traffic.
- Traditional VPN Overhead – Legacy VPN solutions route all traffic back to a single data center (backhauling), increasing latency and impacting user experience.
- Security Inspection Delays – Traditional perimeter firewalls often perform heavy packet inspection, further slowing down traffic.
- No Device Security Posture – Entire communication is monitored based on firewall rules which tracks the Source & Destination IP addresses. But the device that accesses the VPN can get access to entire network and can easily do lateral movement from there.
Why ZTNA is the Answer ?
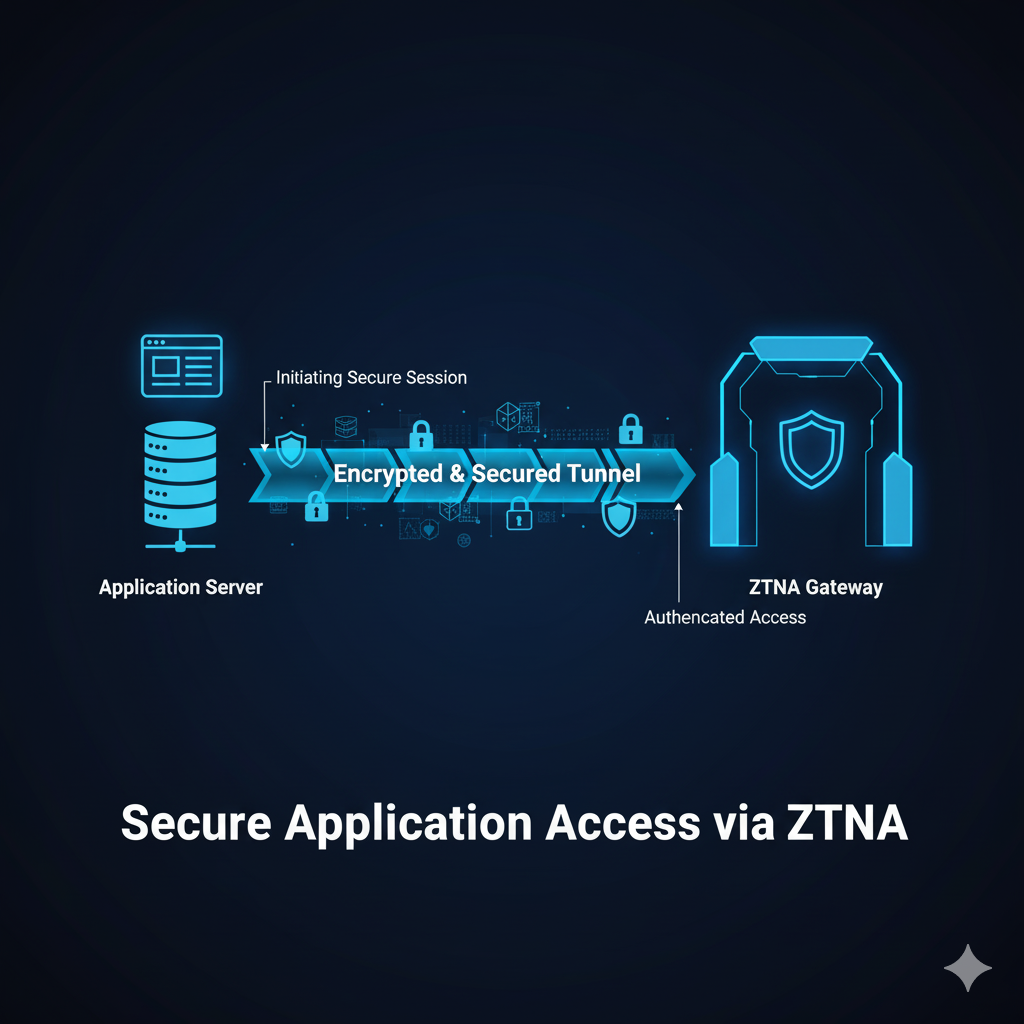
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is a modern approach that replaces the traditional VPN and perimeter-based security model. Instead of connecting users to the entire network, ZTNA connects them only to the specific applications and resources they need — and does so securely from any location.
- Granular Access Control – Users are authenticated and authorized for specific apps, not entire networks.
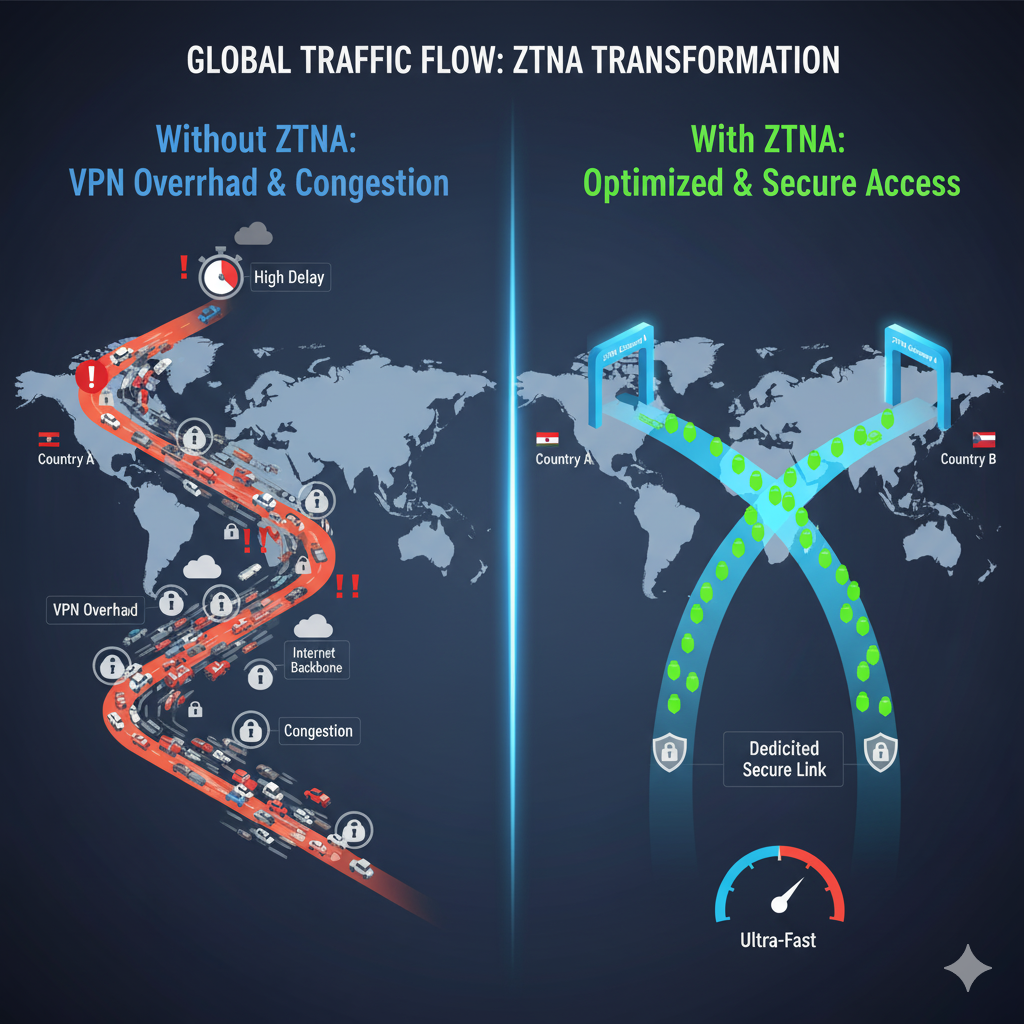
Cloud-Native & Scalable – No need for centralized VPN appliances; traffic is routed through the nearest ZTNA gateway.
- Micro-Segmentation – Applications and workloads are segmented, reducing the risk of lateral movement during a breach.
- Continuous Verification – Access is continuously validated, not just at login. Not just the device but the User who login is used, Which device is used to login, the security posture of the device is monitored.
- Optimized Traffic Flow – Routes user traffic through the nearest edge location, reducing latency significantly.
- Outbound Traffic Connection – One of the important aspects of using ZTNA, We don’t need to Open ports in firewalls to allow the traffic, rather the ZTNA applications goes as an Outbound connection and registers with ZTNA gateway. This closes the loopholes and makes the attacker don’t see any open ports. The connection from the servers where the application hosted will be tunneled to ZTNA gateway.
Get your network assessment done today with Cloud Armor IT Consultancy.
Contact: sampath@cloudarmor.in
Categories

